If you’re starting to notice engine-related issues, you might want to have your fuel pump driver module (FPDM) checked. It’s a critical part of the electronic returnless fuel supply system.
What Is the Fuel Pump Driver Module?
The FPDM or fuel solenoid driver (FSD) controls the voltage supply to the electric fuel pump to ensure the fuel pump gets the right amount of power at a given time.
Vehicles equipped with an electronic returnless fuel supply system usually have an FPDM assembly instead of a fuel pressure regulator.
More on Electronic Returnless Fuel Supply Systems
To understand the role of an FPDM, let’s look at how an electronic returnless fuel supply system operates.
The powertrain control module (PCM) analyzes how much fuel pressure is needed based on the data it collects from various sensors (fuel rail pressure sensor and fuel temperature sensor). The FPDM then controls the fuel pump based on the PCM’s input.
When you start the engine, the voltage goes to the pump through the FPDM or a separate fuel pump circuit. The module controls the fuel pump motor’s ground circuit on a pulse-width modulated duty cycle.
What’s the Difference Between a Fuel Pressure Regulator and an FPDM?
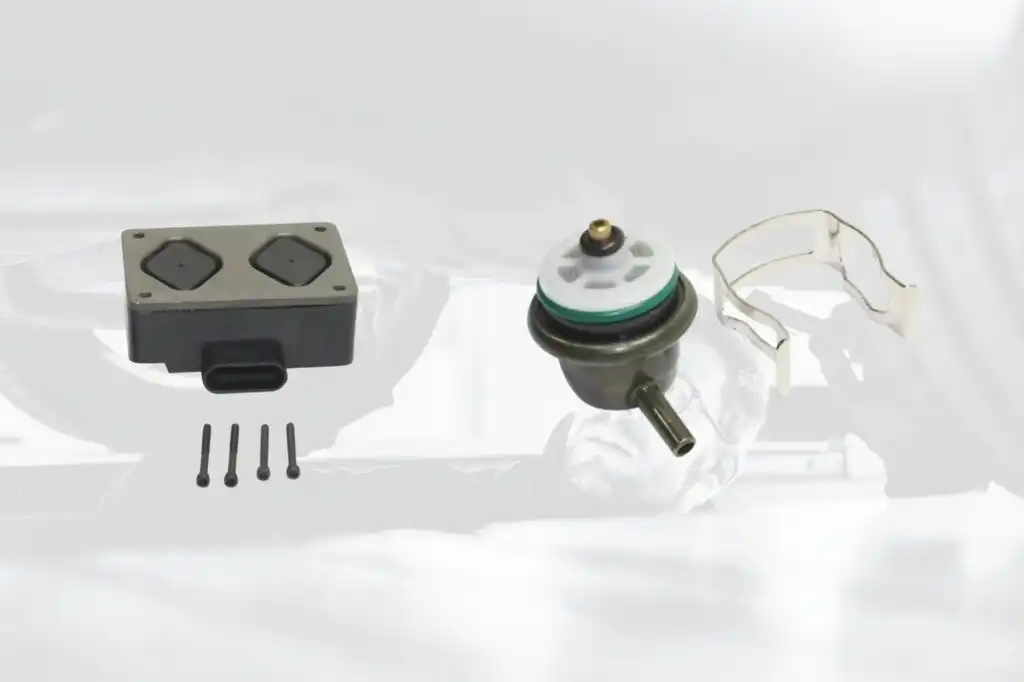

If you own an older vehicle, there’s a high chance that it’s equipped with a fuel pressure regulator instead of an FPDM. What’s the difference between these two?
In older cars, the fuel system maintains a constant high pressure. The fuel pressure regulator is a valve that opens to varying degrees to allow excess fuel to return to the fuel tank. This process goes on, and the fuel pressure regulator adjusts its valve position every time to adjust fuel pressure.
Meanwhile, the FPDM offers a more advanced method of managing fuel pressure. It uses voltage modulation rather than providing a constant 12-volts supply to the pump. By doing this, the FPDM can accurately adjust the amount of fuel being delivered. This enables the pump to provide varying levels of fuel pressure as needed, so there’s no need for a traditional fuel pressure regulator.
The FPDM offers a more advanced method of managing fuel pressure. It uses voltage modulation rather than providing a constant 12-volts supply to the pump.
–Anthony Harlin, ASE Certified Master Automobile Technician
Where Is the Fuel Pump Driver Module Located?
The location of the FPDM varies depending on the vehicle, but it’s usually at the back of the car (on its underside or rear end). You can check out your user’s manual to know where the FPDM is on your vehicle.
Symptoms of a Faulty Fuel Pump Driver Module
FPDMs usually fail due to corrosion, overheating, or road vibration. Here are some of the most common symptoms of a malfunctioning FPDM:
Engine Misfires and Stalling
When the driver module malfunctions, the pump won’t produce the right amount of pressure, causing the engine to run low or misfire. Your engine can also stall because of it.
Damaged Fuel Filter
A malfunctioning module can result in an unstable voltage delivery to the pump. If it pushes too much fuel, it can strain the filter and affect its lifespan and performance.
Engine Surges
If your engine surges or hesitates while accelerating, it can be a sign that the module is malfunctioning. That’s because it might not send the right amount of fuel for engine operation.

Loud Whining Noise
While it’s normal to hear a faint hum coming from the fuel tank, a loud whining noise is concerning. It could mean that something is wrong with the fuel pump. One of the issues that can cause issues for the pump is a faulty fuel pump driver module.
Rough Idling
If you’re having a hard time maintaining a smooth idle, it could mean that your FPDM is starting to malfunction. Remember that this module controls the fuel pump and supports all its functions.
Bad Gas Mileage
The pump will not function as it should once the FPDM gets faulty, so the engine might consume more fuel than usual. If you’re starting to notice that you’re taking more trips to the gas station, it’s time to have your fuel system inspected.
Poor Engine Performance
Your vehicle can’t perform its best if it doesn’t receive the right amount of fuel. If your car doesn’t respond quickly or efficiently when you try to accelerate, it could be a sign that your FPDM is not functioning as it should.
Most of these symptoms can point to other problems. To confirm whether they’re due to a bad FPDM, it’s best to have a mechanic diagnose the issue.
Can You Drive With a Bad Fuel Pump Driver Module?
Driving with a faulty FPDM isn’t safe because it can cause a lot of issues that can make driving difficult. If you suspect that your FPDM is faulty, contact a licensed mechanic immediately. Ignoring this issue can lead to more complex problems that are harder to repair.
How Much Does an FPDM Replacement Cost?
A fuel pump driver module can cost anywhere between $100 and $500. The exact cost of the part can vary depending on your vehicle and the module’s brand. Labor costs will also differ based on your ride’s year, make, and model plus the rates in your area.
Your FPDM is crucial to your vehicle’s operation, so watch out for fuel pump driver module symptoms. Don’t think twice about replacing it if it’s faulty. Take note that your replacement FPDM has to be programmed to your vehicle. So keep that in mind when replacing the module.
Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.