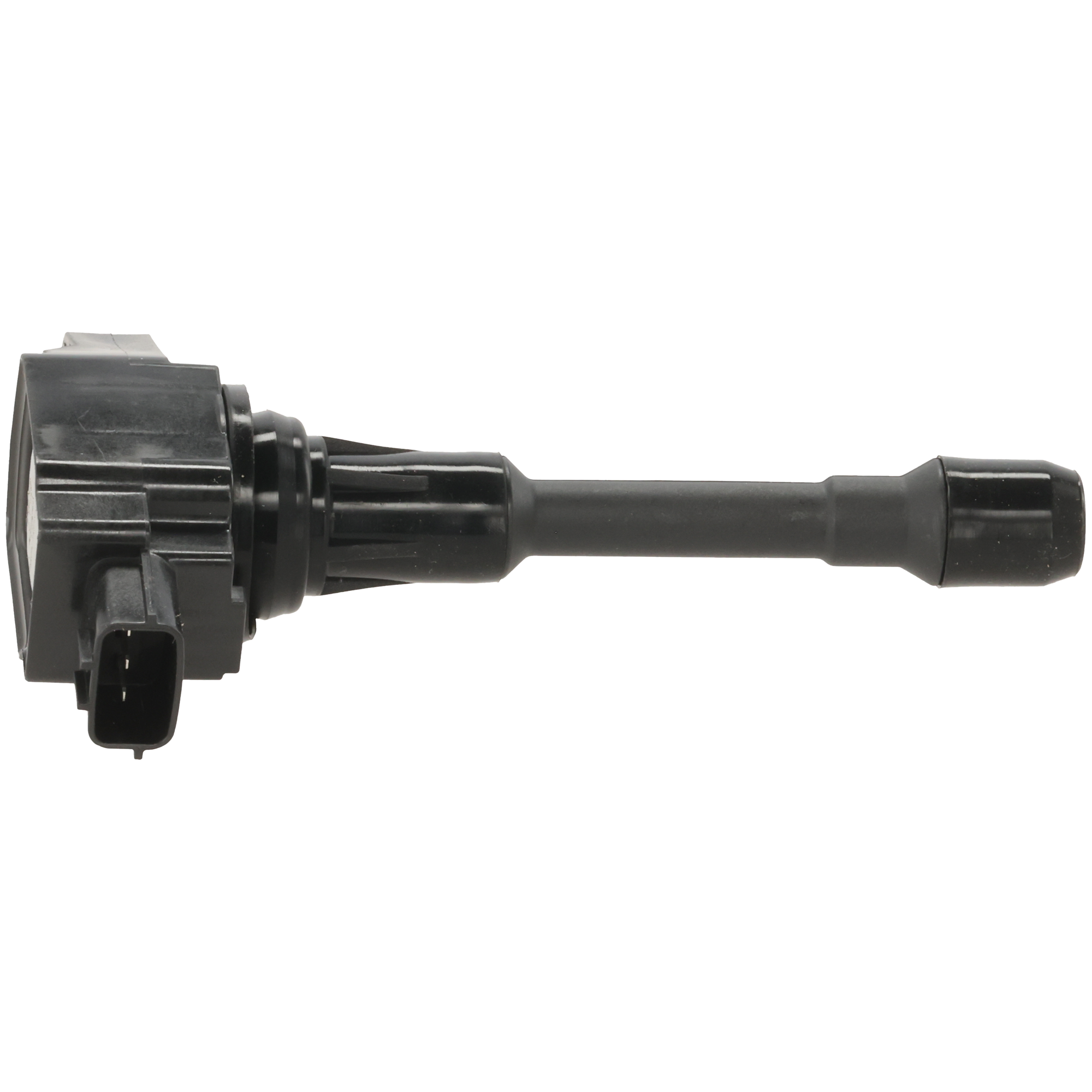
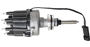
A coil pack, simply put, is an electronically controlled pack of ignition coils regulated by the car’s computer. Learn more about it and read answers to commonly asked questions about the coil pack below.
What will happen if you have a bad coil pack?
Once the coil pack fails, engine misfiring can happen because one or more spark plugs in the engine cylinders didn’t receive enough voltage.
What are the common symptoms of a faulty coil pack?
A faulty coil pack has pretty similar symptoms to a failing spark plug including rough idle, unusually louder engine, a noticeable drop in RPMs when accelerating, and significant lack of power. You might also notice your check engine light blinking in extreme cases.

Coil packs can also fail under load (like at 45 mph in high gear) with the occasional “bite” feeling of an intermittent misfire. This kind of misfire might not even set a misfire code but can be very annoying.
How to make sure that the coil pack isn’t the problem in your vehicle?
Note that the most reliable way to test for ignition coil problems is with an oscilloscope or a scan tool that records counted misfires on each cylinder.
However, there’s a fairly easy test that you can perform to make sure that the coil pack is working properly. What you need to do is to use an ohmmeter to check each coil’s primary and secondary resistance. But just to be clear, this resistance test isn’t 100% accurate – a coil can pass resistance tests and still be the problem if it is leaking high voltage internally – and the meter test won’t show you that.
For the primary resistance, the ohmmeter should be set to the 10 ohms range. Then you need to touch one of the meter leads to the center prong on the electrical connector of the coil pack. If the reading is between 0.3 and 1.0 ohms, then it’s within range, but once again, this isn’t a GO-NO-GO test.

It’s the same thing for the second resistance. This time, however, the ohmmeter should be set to 20,000 ohms. The reading should be between 5,000 and 10,000 ohms. This process should be done on each coil.
Check out these tutorial videos in case you need to replace your ignition coil:
Coil Packs: A Quick History
Note: You can learn about how ignition coils have evolved throughout the years here.
In the mid-80s, distributors began to disappear, replaced by coil packs that fired pairs of “companion” cylinders (those are the cylinders on four-stroke engines where the two companion pistons always reach TDC at the same time). In other words, coil packs fire virtually every time each piston reaches the top of its stroke, but most of the energy is expended in the firing cylinder. This kind of ignition is also referred to as “waste spark” because even during the exhaust stroke, the spark plug fires.
Motorcycles have used this kind of ignition for literally decades, but there are still primary and secondary windings in the coil pack, which receives voltage with the key on and the ground pulse from an ignition module or the ECM/PCM.
Where to Get a New Coil Pack for Your Vehicle
It’s best to stop driving until you’ve replaced your bad coil pack to keep its symptoms from getting worse. Issues like rough idling and reduced power might seem like minor hassles, but they’re often expensive to fix. Lucky for you, finding and getting a new coil pack is easy here at CarParts.com.
Start by entering your ride’s year, make, and model into our vehicle selector to view compatible parts, then use the filters to check out those that match your needs. Get your new coil pack just days after ordering it, thanks to our fast and reliable shipping.
We offer OE-quality coil packs at unbeatable prices, so you’re sure to find one that fits your budget. We accept returns within 60 days of purchase; just file a claim through our returns center for a full refund. So don’t let a bad coil pack ruin your driving experience. Shop for a high-quality replacement today.
Products Mentioned in this Guide
Shop this Project



Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.


 Ignition Coil
Ignition Coil
 Spark Plug
Spark Plug