Antifreeze is stored in the coolant reservoir near the radiator. It’s usually mixed with water in the container, creating what’s commonly known as engine coolant.
Antifreeze is more commonly called “coolant” by professionals. This is a glycol-based fluid that helps regulate the engine’s temperature. When combined with water, it lowers the liquid’s freezing point, enabling coolant to keep flowing at extremely low temperatures instead of turning into solid ice.
Furthermore, antifreeze raises the water’s boiling point, keeping the liquid from evaporating into steam at very high temperatures.
Antifreeze also helps prevent corrosion. It contains additives called corrosion inhibitors that stops rust and other corrosive deposits from forming in the engine. These inhibitors maintain the coolant’s alkaline pH, preventing acidity that can corrode metal.
Warning: To prevent serious burns, never open a hot cooling system under any circumstances. Always feel the radiator hose to see if it has pressure. It’s best to let the engine cool for at least 30 minutes, then check for system pressure by feeling the hose.
Tips on How to Access the Antifreeze
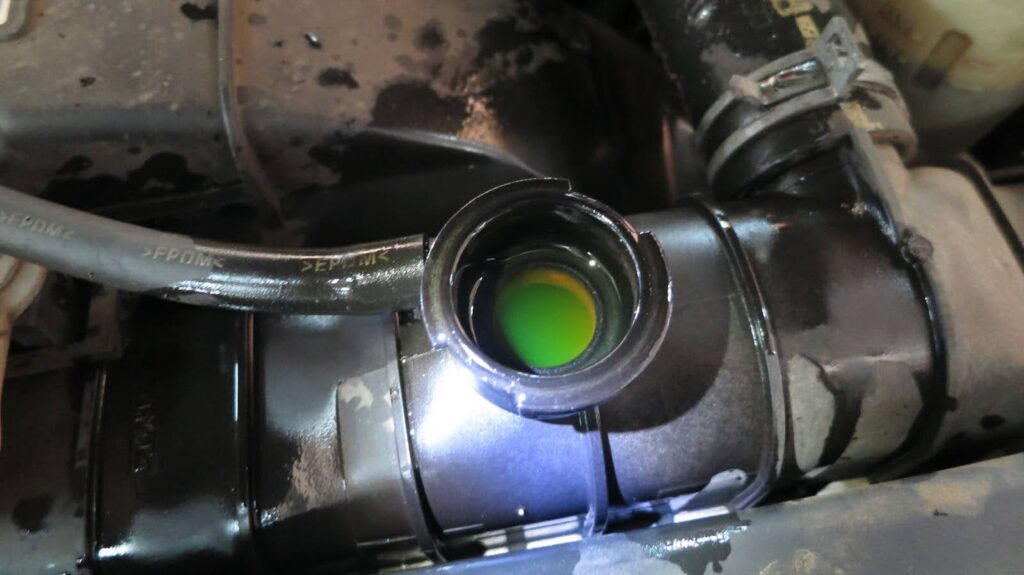

Systems with a thin de-gas bottle may have coolant in the reservoir but have very little coolant in the radiator itself, so you can’t just look at the coolant level in that plastic reservoir to determine coolant level on a system with a cap on the radiator.
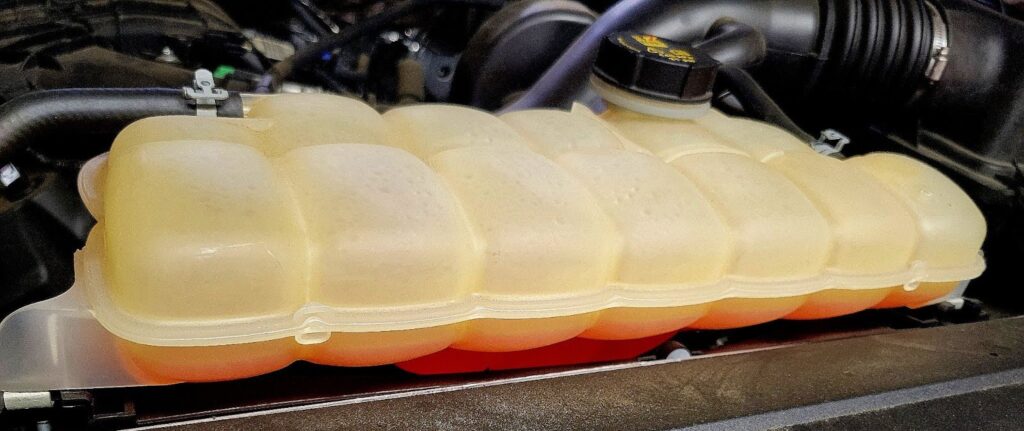
If yours doesn’t have a radiator cap, then looking at the coolant level in the heavy surge tank is the only choice you have, and that’s where you’ll add all the coolant to the system.
On systems with a radiator cap and surge tank, you need to understand that if all the coolant has been drained from the system, refilling the engine with coolant isn’t like pouring water in a bucket. Air will be trapped in the system and it needs to be systematically allowed to escape as the thermostat opens when the engine warms up.

Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.