The radiator is crucial to the overall functionality of your vehicle’s cooling system. When it’s time to buy a radiator replacement, you should be equipped with the necessary know-how to make sure you get the right one.
In this article, you’ll learn all about the radiator— its different types, when it needs replacing, how much it will cost you, and other related FAQs.
How Does a Radiator Work?
Your engine provides your vehicle with power through the burning of fuel and the production of energy from its numerous moving parts. These generate a significant amount of heat which needs to be vented to avoid overheating. Otherwise, the vehicle may suffer from engine damage.
The radiator is responsible for eliminating excess heat from the engine, along with other parts of the cooling system. First, coolant flows through the radiator’s core tubes. Heat is then transferred to the tube wall and soldered joint to cooling fins. The fins are exposed to the air that flows through the radiator, which removes heat from the radiator and carries it away.
The radiator must be capable of removing approximately the same amount of heat energy that is produced by the engine. As the engine power is increased, the heat-removing requirement of the cooling system is also increased.
Types of Radiators

There are two common types of radiators: serpentine fin core and plate fin core radiators. These types are further classified into down-flow and cross-flow radiators.
Down-flow radiators
Down-flow radiators are commonly found in older vehicles. In these devices, the coolant enters the radiator from the top and flows downward, exiting from the bottom of the radiator. They’re typically taller and narrower than cross-flow radiators.
Cross-flow radiators
Modern vehicles commonly have cross-flow radiators where coolant flows from one side to the other. These are generally preferred as they have advantages over the down-flow radiators.
Cross-flow radiators are more efficient at removing heat given their larger core area. They can also keep liquids closer to the core for longer. Double- and triple-pass radiators are usually of the cross-flow variety, meaning coolant can pass over the core multiple times.
However, it isn’t always easy changing your car’s radiator from down-flow to cross-flow. You might need to make a number of other modifications depending on your vehicle’s make and model. It’s usually best to stick to the same flow type when you change your radiator, unless there are significant problems.
Radiator Materials
Radiators can also be classified by material. They are usually made of plastic and aluminum, copper and brass, plastic, or aluminum. The two parts of the radiator–the core and the tanks–can be made of different materials, hence the mix.
If you’re looking for an affordable and basic radiator, a plastic and aluminum radiator might be the right one for your ride. This stock hardware has core parts made of aluminum and tanks formed from plastic. Most car radiator replacements will be this type.
However, if you want one that is built to last and don’t mind paying extra, you should consider getting an aluminum radiator for your ride. These radiators are used for more high-performance vehicles such as racing and muscle cars.
Radiator Rows
You should also consider the number of rows when buying replacement radiator parts for your car or other vehicle. These rows control how much coolant passes through the core and how much air can contact the coolant.
Typically, more rows mean more heat dissipation, but adjustments can still be made. For instance, copper and brass radiators tend to have more rows, while aluminum radiators will make up for their lack of rows with added fins and tubes.
Now that you know the different kinds of radiators, you might be wondering, how can you tell when it’s time for a replacement?
Signs of Radiator Failure
Over time, your vehicle’s radiator will naturally start to break down due to the intense heat and stress it’s constantly under. When this happens, you’ll likely notice some of the following symptoms of an inoperative radiator:
- An overheating engine
- Coolant leaks beneath the vehicle
- Shifting issues from coolant contamination in the transmission
- Coolant discoloration
- Blocked exterior radiator fins
- Inoperative passenger heater
- Inaccurate instrument cluster temperature gauge
- Smoky smell from under the hood
- Visual rust evidence
If you start seeing these signs, it’s time to consider either repairing or replacing your vehicle’s faulty radiator.
Is It Worth Replacing a Radiator?
A faulty radiator should always be replaced as soon as possible to prevent overheating and possible engine damage.
For those looking to make this a DIY project, it’s also important to know how long it takes to replace a radiator. Those who are familiar with automotive projects can do it in two to three hours, but for those who aren’t as savvy with cars, the job might take up about half a day. It’s up to you to decide whether to replace a radiator yourself or call a trusted mechanic.
How to Replace a Radiator in a Car

If you’re confident in your automotive know-how, replacing your radiator yourself is an option. Before attempting any fixes, remember to read your vehicle’s repair manual or look up vehicle-specific repair information from an online database.
Here’s are the tools you will need:
- Screwdriver and/or pliers
- Drain pan
- Safety gloves and goggles
- Car jack and jack stands
- Socket, ratchet, and extension
- Flare nut wrench
- Cooling system vacuum fill tool

Step 1: Prepare your vehicle, tools, and safety equipment
Review your vehicle’s repair manual before starting any repair work. Make sure the engine has cooled down and wear the appropriate safety gear before raising your vehicle. This gear typically includes a set of protective gloves and eyewear.
Step 2: Raise your vehicle and provide proper support
Your vehicle needs to be raised off the ground in order for its radiator to be removed. Apply the parking brake and use jack stands to make sure your vehicle is secure and properly lifted.
Step 3: Drain all of the coolant
Drain all of the coolant from the old radiator into an approved container. The most accessible option is made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
Remember that after handling coolant, you should wash your hands thoroughly to avoid chemical damage. If any should splash on your skin, wash it off immediately as well.
Step 4: Disconnect and remove the old radiator
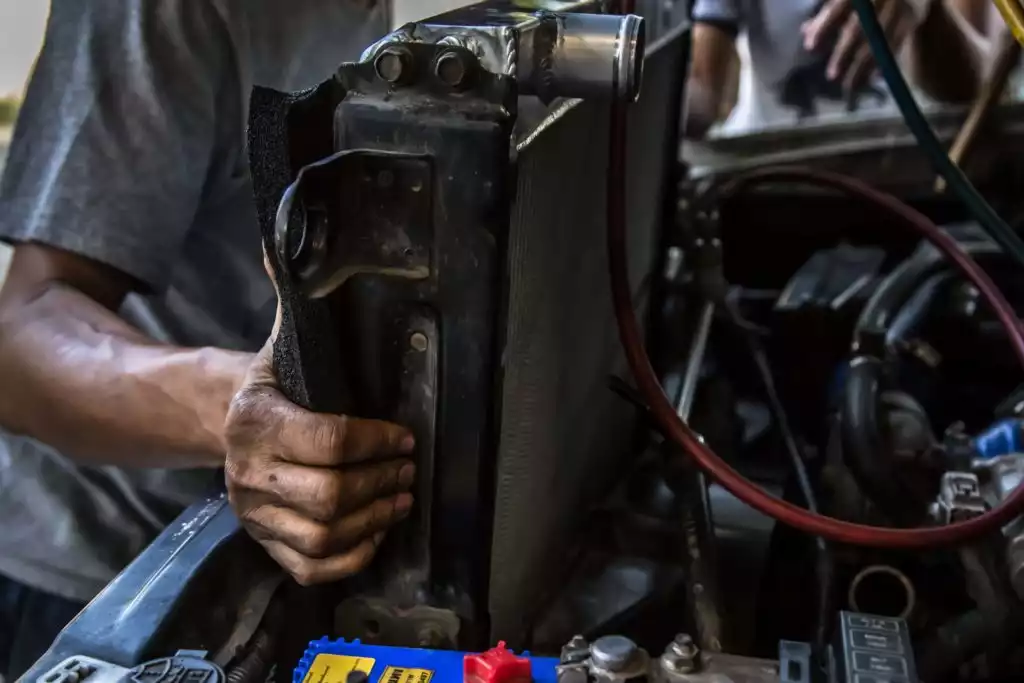

Most vehicles will need these parts disconnected before removing the old radiator:
- Reservoir hose
- Upper and lower radiator hose
- Cooling fan electrical connector
- Cooling fan
- Transmission cooler lines
- Mounting bolts
Once disconnected, the old radiator may be removed by lifting it up and out or by moving it from below the vehicle.
Step 5: Install the new radiator
Reconnect the parts mentioned in the previous step. Use this opportunity to inspect them for leaks or damage and replace them as needed.
Step 6: Refill radiator with fresh coolant
Fill your new radiator with coolant according to manufacturer specifications. Bleed any trapped air out of the system.
Warning: If you do not properly bleed the air from the cooling system, overheating and engine damage may result.
Step 7: Recycle coolant
Bring the drained coolant to a local shop for recycling.
For a more in-depth discussion of how to replace a radiator, read this article.
What to Consider When Looking for a Radiator Replacement
Shopping for a radiator replacement for a car can become overwhelming because of the many options available. To help you choose the right fit for your vehicle, here are some factors you should consider:
Application
Don’t forget to check your vehicle’s specifications before buying a new radiator for your ride. Getting a replacement designed for your vehicle’s year, make, and model guarantees a perfect fit and hassle-free installation.
Quality
Choose a brand you trust when looking for a new radiator for your ride. A radiator is crucial to the functionality and overall operation of your vehicle, so the replacement should be durable and made of high-grade materials.
Finding the perfect replacement radiator for your vehicle should be easy as long as you follow the tips listed above and look through credible product reviews. Remember to check your vehicle specifications or consult your trusted mechanic.
Here’s a helpful video on how to replace your radiator:
Preventive Radiator Maintenance
Prevention is always going to be better than replacement or repair. Properly maintaining your vehicle’s radiator is the key to keeping it running for as long as possible.
Remember to replace the radiator hoses every 3 years or 36,000 miles. The hoses can crumble over time, leading to radiator issues.
Also, keep your radiator topped up with coolant. Check the coolant levels regularly and check for leaks if it drops too often. Make sure you refill the coolant using the correct coolant concentration.
Finally, don’t forget to have the coolant flushed every 25,000 miles to get rid of contaminants in the system. This’ll keep debris from building up in the lines and causing issues later on.
Where to Get a Replacement Radiator
If your radiator develops a problem, it’s best to stop driving your vehicle until you can get a replacement. Driving with a bad radiator can lead to additional engine issues, which generally cost a lot to fix. Fortunately, you can quickly get your car or truck back on the road with a replacement radiator from CarParts.com.
Why line up at the checkout counter when you can access CarParts.com through your mobile phone from the comfort of your home? Plug the details of your car or truck into our vehicle selector, and you can browse the search results for the right radiator that fits your application. Once you confirm your order, you simply have to wait for a few business days for your new part to arrive at your doorstep. Furthermore, you can rest assured that your replacement radiator fits your car and delivers the cooling performance you need because we only source our products from the industry’s most trusted brands.
CarParts.com carries a wide selection of radiators, one of which is sure to fit your car. Check out our selection and order a radiator today.
Shop this Project



Any information provided on this Website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace consultation with a professional mechanic. The accuracy and timeliness of the information may change from the time of publication.